Radiology Services
Both 2D & 3D imaging including MRI
Evaluation of periapical radiographs, bitewings, panoramic radiographs, CBCT imaging of all fields of view, and MRI of the TMJs
Endodontics
Endodontic evaluation typically includes finding missed canals, root fractures, persistent apical inflammatory processes with possible sinus tracts, etc
Orthodontics
Orthodontic evaluation typically includes evaluating impacted dentition, evaluating the primary dentition, supernumerary teeth, airway measurements, evaluation of the temporomandibular joints, evaluation of possible resorption of the dentition, evaluating crown to root ratios of dentition for unfavorable ratios which may contraindicate orthodontic treatment
Pediatrics
Pediatric evaluations typically include assessment of the pharyngeal and palatal tonsils as well as the primary and secondary dentition including missing or supernumerary teeth. The temporomandibular joints and sinuses are always evaluated for any abnormalities, asymmetry etc. Analysis of the airway for increased risk factors of obstructive sleep apnea has become more frequent in pediatric patient's as studies have shown a possible genetic correlation.
TMD
Evaluation of the temporomandibular joints for remodeling, osteoarthritis (active and inactive), idiopathic condylar resorption, possible rheumatoid arthritis, internal derangement of the articular discs (requires MRI for direct visualization of the discs due to limitations of CBCT imaging in soft tissue diagnosis)

Pathology
Evaluation of the hard and soft tissues for any evidence of localized or systemic pathology including odontogenic cysts among numerous other processes
Dental Implants
Evaluation of anatomy in the area of implants, including the quality and quantity of bone, relation to vital structures including the mandibular canal and the sinuses, and evaluation of possible graft material
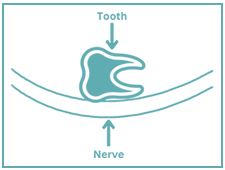
Impacted teeth
Evaluation of impacted teeth to vital structures and their exact locations within the maxillae and mandible, evaluation of adjacent teeth for possible resorption
General Evaluation
General evaluations typically include imaging of the airway, the TMJs, the maxillary sinuses, and the nasal cavity, with a panoramic reconstruction
Airway assessment (oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal)
Airway measurements of the oropharyngeal and nasopharynx (these measurements are not always reliable as many factors including musculature, patient positioning, and whether the patient is expiring/inspiring during the scan affect the airway dimensions), the evaluation also includes identifying hyperplastic tonsils as well as the pharyngeal recesses and any asymmetry

Incidental findings
Incidental findings are common and may include osteomas, tori, exostoses, sialoliths, tonsilloliths, carotid calcifications, etc
Pathology Services
Online image consultation (Texas)
Images can be sent via the portal for an online consultation via zoom
Clinical image submission with differential diagnosis (Texas)
Images can be sent via the portal for an in-depth evaluation of the soft tissues and a differential diagnosis to further narrow down the possible pathology process and help determine whether a biopsy is required
In-person consultation/Oral medicine treatment (Austin, Texas)
An in-person consultation can be requested to evaluate the patient’s hard and soft tissues, an intraoral and extraoral exam, identification of pathology, as well as oral medicine treatment including xerostomia, soft tissue growths, red and white lesions ex. lichen planus, desquamative lesions, etc ·
Biopsy (Austin, Texas) and submission of pathological specimen to one of three pathology services in Dallas, Texas
An in person biopsy can be requested for the removal of a sample of tissue after thorough evaluation. The biopsy types include incisional, excisional or a punch biopsy and depend on the clinical situation as well as the biological process and the differential diagnosis (multiple sites may be required for a case with a suspicion of squamous cell carcinoma)